Related

This article is written by Bryan N. Duncan, Carl A. Malings, K. Emma Knowland, Daniel C. Anderson, Ana I. Prados, Christoph A. Keller, Kevin R. Cromar, Steven Pawson, and Holli Ensz and published in GeoHealth.
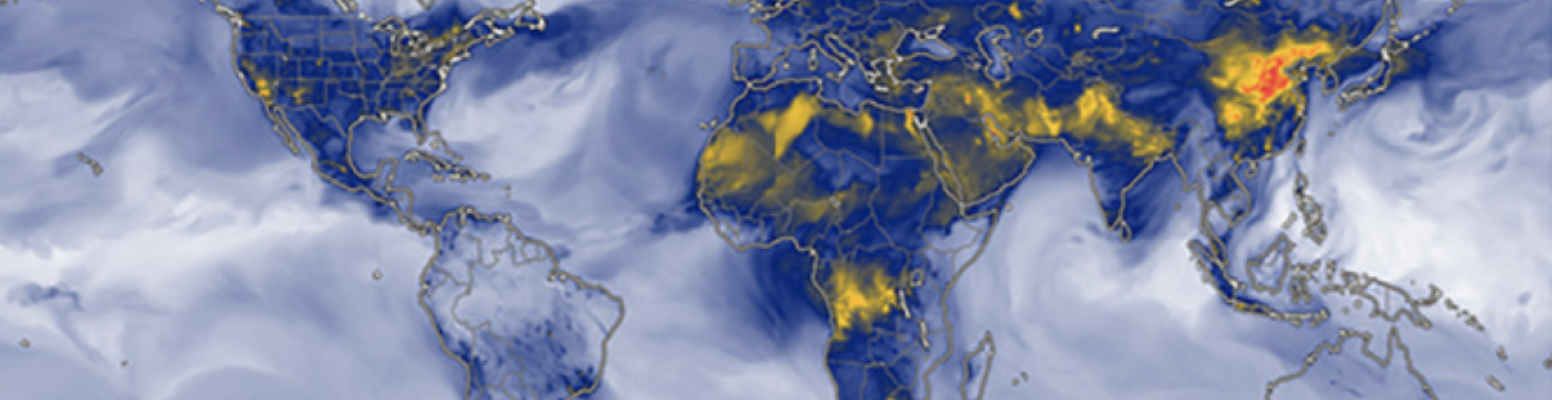
The combination of air quality (AQ) data from satellites and low‐cost sensor systems, along with output from AQ models, have the potential to augment high‐quality, regulatory‐grade data in countries with in situ monitoring networks and provide much needed AQ information in countries without them, including Low and Moderate Income Countries (LMICs). We demonstrate the potential of free and publicly available USA National Aeronautics and Space Administration (NASA) resources, which include capacity building activities, satellite data, and global AQ forecasts, to provide cost‐effective, and reliable AQ information to health and AQ professionals around the world. We provide illustrative case studies that highlight how global AQ forecasts along with satellite data may be used to characterize AQ on urban to regional scales, including to quantify pollution concentrations, identify pollution sources, and track the long‐range transport of pollution. We also provide recommendations to data product developers to facilitate and broaden usage of NASA resources by health and AQ stakeholders.
Please fill out the information below to receive our e-newsletter(s).
*Indicates required.